8 Ways Automation Is Changing the Logistics Industry

Logistics automation helps simplify and streamline the various steps of the supply chain. Circuit for Teams helps automate delivery route planning and management.
Technology has made our lives easier in a lot of ways, from allowing online shopping to simplifying digital payments. Cutting-edge innovations are changing industries and economies around the world — and the logistics sector is no exception. Automation is one trend that’s helped reshape the field.
Logistics automation refers to the use of technology to make logistics processes more efficient by automating them so minimal human intervention is needed.
These days, automation-related advancements are found in mostly every step of the supply chain, from warehousing to inventory management, distribution, and more.
As a logistics professional, learning about the opportunities offered by logistics automation can help you streamline your everyday workflows. That means less tedious workloads, faster operations, and saved resources.
Read on to learn what logistics automation is, why it’s important, and where it can be implemented.
Key takeaways
- Logistics automation refers to the use of technology to automate and streamline logistics processes, reducing the need for human intervention.
- Automation has many benefits for logistics providers, from improving efficiency to reducing the risk of human error and cutting costs.
- Automation can be applied to various areas of logistics like warehousing, workflows, and inventory management.
- Learning about automation's uses can help logistics professionals keep up with evolving market demands and maintain a competitive edge.
What is logistics automation?
Logistics automation refers to the use of technology to make the various steps of the logistics process more efficient. Such technologies could include machinery, robotics, software, hardware, artificial intelligence (AI), and more.
An example of logistics automation would be a robot used to automatically pick products from warehouse shelves.
There’s no need for a human to find the products. If the warehouse is properly organized and the robot picker is correctly programmed, then the machine can find the product to pick and pack.
Automation might sound like it’s new, but it’s been shaping the logistics industry for decades.
Historical automation developments in the transportation and logistics sector include GPS tracking of deliveries, the use of QR codes to sort and track products, and self-driving warehouse machinery.
Software developments have also contributed to transportation and logistics automation. Modern software tools for supply chain management help with things like inventory management.
For example, if inventory levels fall below a certain level, a tool can be set to automatically reorder inventory.
Why is automated logistics important?
Pro tip: If you’re in the logistics business, automation can save you a lot of headaches.
In the past, the traditional logistics landscape required a lot of tedious humanpower. Take something like last-mile delivery — the process of getting packages from a warehouse to the customer’s doorstep.
Historically, businesses would have to use maps to chart delivery routes, manually assign them to drivers, and then trust that the packages arrived as planned. That kind of process was time-consuming and left a lot of room for error.
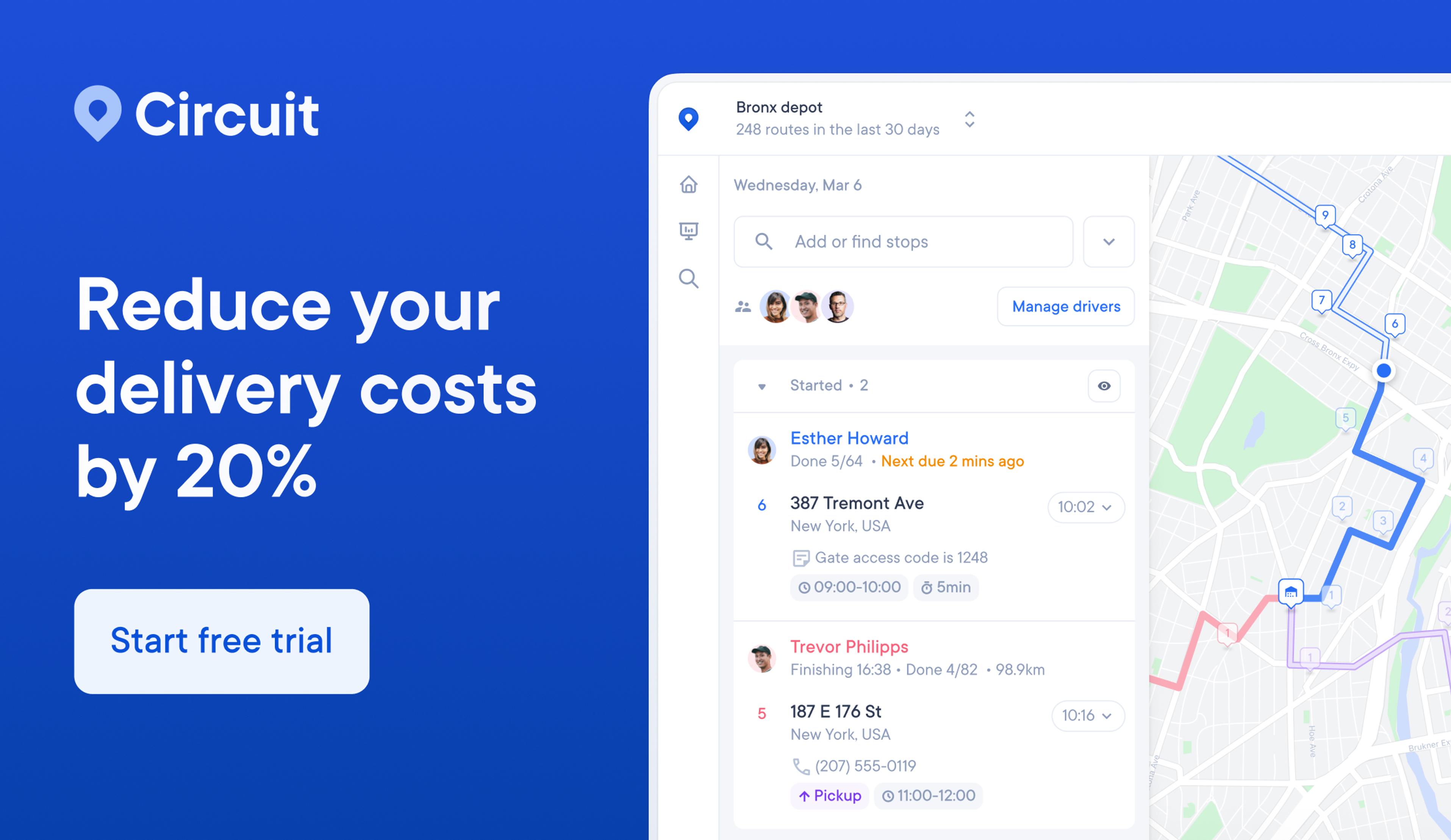
These days, business owners have it a lot easier. They can use route optimization software like Circuit for Teams to automatically chart out the fastest routes, assign them to drivers, and track route progress (by GPS) step by step.
This is just one way that automation has eliminated the traditional hurdles faced by the transportation and logistics industry.
As the sector continues to grow — it’s expected to reach a global market size of $18.23 trillion by 2030 — automation will become even more invaluable, helping businesses deal with larger demand.
Here are some ways that automation is already helping the industry:
- Improving efficiency. Automation can help speed up logistics processes. Tasks that once took hours can be done in minutes. Take a process like unloading pallets. Research from Credit Suisse estimated that unloading a truck of 20 to 26 pallets would take 30 to 40 minutes with humanpower. With automation, this time can be reduced to as little as three minutes.
- Reducing error. Human error can be a major drain on the logistics industry. Experts like McKinsey suggest that automation can reduce human errors in logistics. Credit Suisse’s data supports this. For example, picking the wrong item accounts for some 30 percent of picking mistakes. Automated scanning technologies help shrink these numbers.
- Cutting labor needs. Research from the American Economic Association shows that automation technology reduces the need for human labor while at the same time enhancing productivity. Gadgets like automated guided vehicles (AGVs) — essentially self-driving cars — used in warehouses are one example.
- Saving money. Companies can save cash by automating repetitive tasks. Money savings can also come from reduced labor costs and the ability to optimize resource utilization. For example, McKinsey suggests that calculating material-resource needs can be automated, potentially boosting savings.
- Enhancing scalability. By improving process speed and reducing the need for human labor, automated logistics also improves scalability. Businesses can use technologies to grow without needing to up labor or other costs.
- Promoting adaptability. The use of automation can also help businesses evolve more quickly to meet changing market needs like eCommerce. For example, McKinsey flags the rise of same-day delivery — as an area where automation can help companies keep up.
- Improving safety. Automated machinery can work in environments that might be hazardous to humans, which promotes safety. Manufacturing & Logistics IT Magazine flags hazards like dust as dangers and explains how automation tools — like robotics and drones — can take dangerous tasks off human hands.
- Improving data collection and analysis. Automation gives companies the chance to collect vast amounts of data, which can be analyzed for business insights and inform future decision-making. For example, software that tracks inventory can generate reports used for forecasting consumer demand, which can then be used to plan for future stock levels.
- Better environmental outcomes. Automation can even help save the environment! Take something like delivery driver route planning. By using route optimization software, companies can chart the fastest routes for drivers, cutting down on needless mileage and fuel waste. The result? A smaller carbon footprint and a happier planet!

Areas where automation is streamlining logistics operations
Have we sold you on the benefits of automation for logistics operations? Good. The next question is exactly how you can implement automation in your workflows.
Here are some ideas for automating logistics operations to inspire you.
Warehousing
Warehousing has been simplified and made more efficient with machinery like automated storage, robotic arms (for picking and packing products), and conveyor systems (for moving products).
Barcode technology is another enhancement, making it easier to avoid errors in order picking.
Credit Suisse flags the utility of radio frequency scanning devices (RFID) for automating picking and reducing mistakes. The most common mistakes they cite with nonautomated processes are item omissions, incorrect items, miscounting quantities, and misreading or incorrectly transposing quantities.
Their data suggests that RFID automation systems can achieve accuracy rates of 99.3 percent to 99.5 percent.
Workflows
Automation solutions have streamlined logistics management, notably with the introduction of logistics management software. This can help optimize workflows in logistics operations, from receiving goods to ordering inventory.
Take something as basic as data collection.
McKinsey estimates that data collection and processing have the potential for automation of 60 percent or more. Workflows that could be impacted include procurement, payroll processing, invoice generation, materials tracking, and more.
Inventory management
The implementation of warehouse management systems (WMS) can help simplify the organization and oversight of goods in warehouses. In addition to saving time, a WMS can help reduce the risk of errors like loss and damages and, in the process, save your organization money.
LBM Journal details the ways a WMS can help cut costs. Points include ensuring inventory accuracy, barcode-automating data entry, improving productivity, simplifying cycle counting, and enhancing shipping accuracy.
Material handling
Logistics companies can use automation machinery to save humanpower and improve efficiency. Examples of relevant technologies include palletizing robots, mobile robots, advanced forklifts, and AGVs.
According to Supply Chain Dive, Amazon has long been at the forefront of warehouse robotics innovations like these.
For example, the eCommerce giant is now testing free-roaming robots to move oversized and bulky items within their fulfillment centers. The robots use AI and computer-driven vision.
Learn how to further optimize your material handling.
Distribution
Traditional warehousing is falling by the wayside in favor of fully automated distribution centers. Software solutions can now optimize distribution and reduce the need for hands-on human intervention.
If you’re a ketchup fan, you’ll like this example: Kraft-Heinz is working on a $400 million automated distribution center in Illinois. The modern warehouse will feature end-to-end automation, including automated storage and retrieval systems.
The same article reveals that 26 percent of warehouses are anticipated to be automated as early as 2027.
Order fulfillment
Real-time data and automation technologies can help with various steps of the order fulfillment process, from order picking to creating shipping labels and even sticking them onto packages for shipment.
By getting orders fulfilled faster, businesses can up their order volume without wasting resources.
Again, Amazon is a great example of how order fulfillment can be automated and optimized. Amazon’s Relational Database Service (RDS) automates all kinds of administrative tasks around order fulfillment — from hardware provisioning to database setup.
With a preconfigured database, it’s easier to scale up and maintain business growth.
Supply chain management
AI is refining logistics processes related to supply chain management. For example, using algorithms, AI-driven tools can estimate inventory forecasts and fine-tune procurement.
Research from the Journal of Service Science and Management suggests that AI can optimize logistics and transportation and identify supply chain inefficiencies. Data suggests that time- and cost-savings will only improve as AI improves.
Discover how else to optimize your supply chain.
Third-party logistics
Third-party logistics (3PL) is the process of outsourcing logistics processes to an external provider. This could include warehousing, inventory management, and order fulfillment.
The 3PL market is growing in parallel with the growth in logistics and transportation. Automation is helping 3PL providers keep up, making it easier to manage all the points described above.

Automate last-mile delivery with Circuit for Teams
Logistics automation uses technology to streamline supply chain processes in all kinds of areas, from warehousing to order fulfillment. The benefits are varied, from improving efficiency and reducing the risk of human error to saving money.
If you’re in the logistics business, you should educate yourself about these innovations — or else you risk falling behind the competition.
One tool every logistics manager should know about? Circuit for Teams.
With Circuit, you can automate your delivery routes. Instead of having to figure out routes yourself using a list of customer addresses and an online map, you can simply upload a spreadsheet of addresses into Circuit.
The software then creates ready-made routes, taking into account details like traffic jams and construction sites to figure out the fastest route automatically — no strategizing is needed on your part.
Circuit also works with your favorite GPS technology to track driver routes, so you don’t have to call or text drivers to find out where they’re at. You can just check Circuit.
The software can also be set up to send automated delivery updates to customers, keeping everyone in the know.
Get smart about last-mile delivery. Try Circuit for Teams for free.


