A Timeline of Amazon Last-Mile Delivery

Manage your business’s last-mile delivery as easily as Amazon with Circuit for Teams.
When you order something online, you want to get your hands on it ASAP.
You aren’t alone.
In fact, 75 percent of US consumers are happy to pay extra to get their goods faster — clearly, we all have a need for speed.
One reason fast shipping has become the norm? Blame Amazon.
No, seriously: Amazon is renowned for its fast delivery services and has been credited (more than once) with driving consumers’ high expectations.
After all, services like Amazon Prime have made same- and next-day delivery the standard.
That said, it’s taken time for Amazon to perfect its last-mile delivery process.
Below, I break down Amazon's last-mile delivery development history.
I also highlight some lessons we can learn from Amazon’s delivery evolution.
These tips can be useful for anyone looking to improve order fulfillment, including delivery managers, eCommerce shops, and logistics companies.
What is Amazon last-mile delivery?
Last-mile delivery refers to the final step in the supply chain process — when products make it to the actual customer.
Some companies outsource last-mile delivery to third parties.
For example, your eCommerce shop might use a service like USPS, FedEx, or UPS to send goods to customers.
Amazon has its own last-mile delivery service.
Instead of relying on third parties, Amazon has its own drivers to deliver packages to customers.
The eCommerce giant fills gaps in its driver team with delivery service partners (DSPs), independent businesses that partner with Amazon to get packages to customers.
(Here are six things to know about the Amazon DSP program.)
This allows Amazon to expand its reach and speed up its last-mile delivery.

The history of Amazon last-mile delivery
Amazon’s speedy delivery process has taken years to perfect.
Here’s a quick rundown of the company’s last-mile delivery history.
2009: Same-day delivery
In 2009, Amazon introduced Local Express Delivery, a same-day delivery service.
The offering was limited at first, restricted to just seven cities:
- New York City
- Philadelphia
- Boston
- Washington, D.C.
- Baltimore
- Las Vegas
- Seattle
Amazon slowly expanded its same-day delivery services over the next four years, thanks in part to tech investments — like the acquisition of Kiva Systems in 2012.
As a result, Amazon put robotics into its fulfillment centers, allowing for faster product picking and packing and making same-day delivery even easier.
2013: Operation Dragon Boat
In 2013, Amazon showed off its robotics experience with “Operation Dragon Boat.”
Amazon Prime Air launched with 30 drones, intended to simplify last-mile delivery.
Unfortunately, regulatory issues — like air traffic guidelines — stalled the project.
But it looks like it’s coming back to life (more on that below).
2014: Buying 25 percent stakes in Yodel and Colis Privé
Due to rapid expansion, Amazon had to take steps to keep up with customer demand.
To help keep last-mile delivery on track, the company purchased a 25 percent stake in the shipping company Colis Privé and a 4.2 percent stake in the shipping company Yodel.
This move allowed Amazon to build out its own delivery services.
2015: Amazon Prime Now
Amazon ramped up its commitment to speedy delivery with the introduction of Amazon Prime (then called “Amazon Prime Now”) in 2015.
With the new initiative, Amazon offered expedited services like one-hour, two-hour, and same-day delivery.
The company added at least 58 delivery hubs across the United States to fulfill that tight time frame.
2016: Colis Privé acquisition
Amazon wasn’t happy with just 25 percent in Colis Privé.
In 2016, Amazon bought the remaining 75 percent of the French delivery company, acquiring it completely.
This helped further build out the company’s last-mile delivery services.
2018: Amazon Logistics launch
In 2018, Amazon formalized its last-mile logistics with Amazon Logistics.
This allowed the company to reduce its shipping and fulfillment — which had reached a whopping $61 billion combined by 2018.
2019: Free One-Day Delivery
One common issue consumers faced when picking shipping solutions in the past was speed versus cost.
Do you want to pay extra for something to get there faster, or would you rather save your money and wait?
Amazon solved the age-old problem by offering free one-day deliveries in 2019.
The move cost the company more than $3 billion.
However, it also increased sales and drove up Amazon stock, showing the benefits of investing in improvements that meet consumer demand.
2020: Amazon Robotics Program
Amazon further leaned into the potential power of robotics in 2020 with its Amazon Robotics Program.
The “upskilling” initiative offers training in robotics through hands-on apprenticeships.
Participants learn the skills they need to fulfill technical maintenance roles, for example, as robotics technicians.
These people will become invaluable in the future, as robots become bigger in Amazon distribution centers and shipping operations.
2021 to now
Amazon remains well-known for its fast delivery services and continues to expand and evolve its offerings.
For example, that drone delivery project mentioned above?
Despite the delays, it looks like the program may finally take off (pun intended)!
Amazon hit another milestone in 2022 when it developed its first fully autonomous mobile robot (AMR), Proteus.
Proteus will make Amazon warehouses more efficient, making it faster to pick and package products — and get them to consumers sooner.
The Proteus project’s roots can be traced back to Amazon’s acquisition of Kiva Systems — all the way back in 2012.
As it continues to fine-tune its processes with the help of new technologies, Amazon will undoubtedly stay at the forefront of last-mile delivery.

What can we learn from Amazon last-mile delivery services?
Amazon has evolved its last-mile delivery services significantly over the years.
What can you learn from its evolution?
Here are some takeaways that can help you improve your capacity planning and last-mile delivery:
- Take a customer-centric approach. Amazon recognized consumers’ demands for fast delivery and responded with initiatives like Prime, offering expedited same-day, one-day, and two-day services. Like Amazon, make sure you’re giving customers the conveniences they want. For example, perks like delivery time windows can be handy for your customers, alerting them so they know when to expect a package.
- Seize control of your delivery operations. Amazon has consistently dedicated time and money to expanding its own delivery operations instead of relying on third-party logistics providers (3PLs). Managing your own package delivery operations can give you greater control and save you money since you won’t have to pay a 3PL.
- Make the most of new technology. Amazon is always investing in cutting-edge tools — from drones to robots. While small-business owners and entrepreneurs may not have the budget for cutting-edge tech, they can still use other tools to make their delivery business run smoother. For example, a route optimization tool like Circuit for Teams lets you plan fast delivery routes for your drivers, saving you time and money.
- Train your workers. Amazon recognizes that using technologies like robots involves retraining workers — and the company invests in its people accordingly. You can take a page out of the company’s book by making sure you train delivery drivers and others involved in your delivery logistics. For example, if you use routing software like Circuit for Teams, make sure your workers know how to use the driver app.
- Keep developing. Amazon has been working on its last-mile delivery process for years. Similarly, you should regularly revisit your last-mile delivery processes to make sure they’re still working for you. Do you need to address any bottlenecks? Is there new technology you could use? Could your workers use retraining? These questions can help guide positive business development.
Managing your own team? Discover why the best companies are using Circuit for Teams
Amazon is a role model for speedy delivery, having established a well-known reputation for getting customers the goods they want fast.
However, it's taken the company years to perfect its last-mile delivery process.
A look at Amazon’s evolution of delivery services can be useful for anyone looking to improve order fulfillment — from delivery managers to shipping companies and eCommerce shop owners.
Amazon has important lessons to teach, like the value of meeting consumer demands and investing in your own logistics.
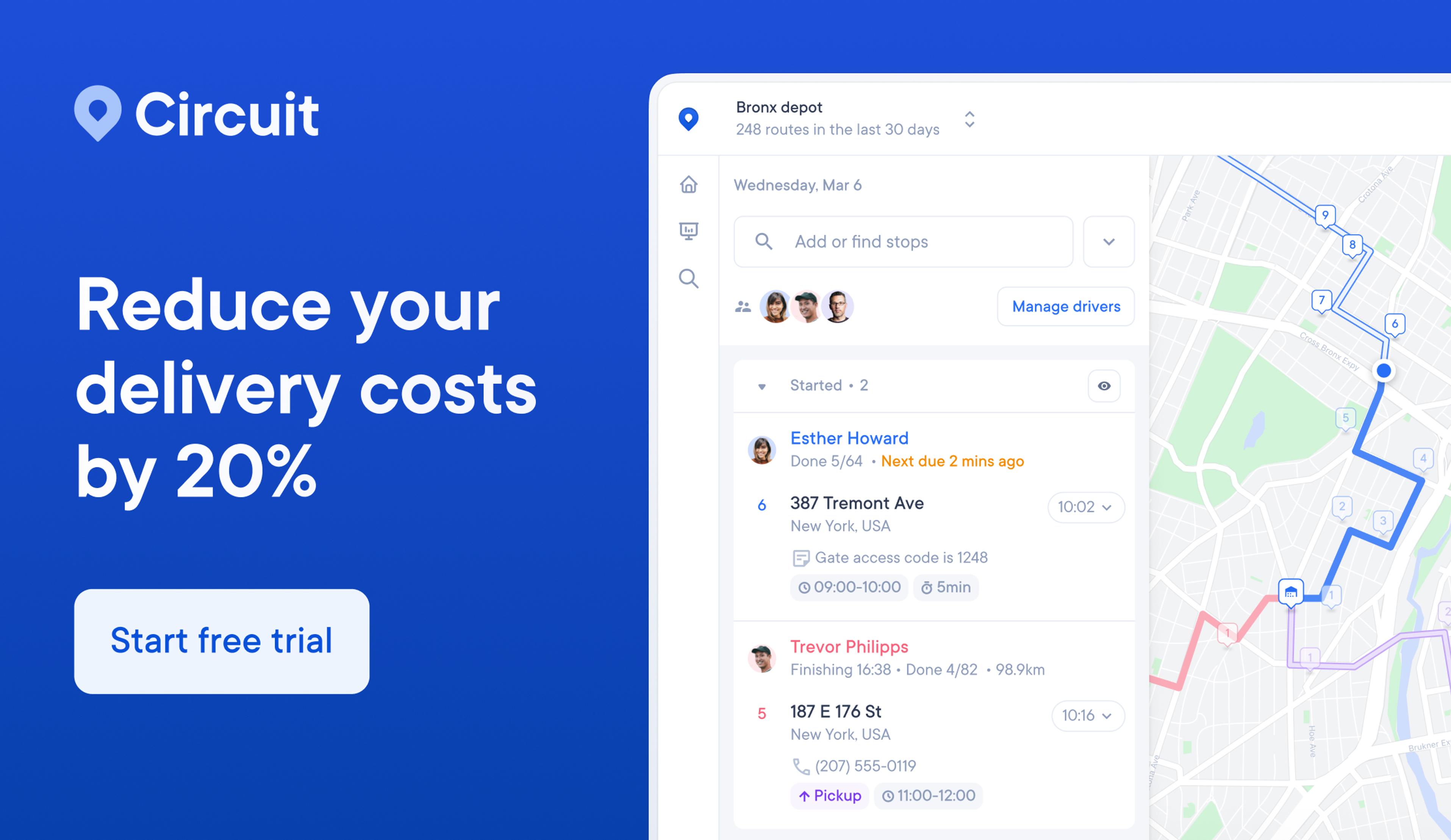
Another thing you can do to stay on the cutting edge and keep your deliveries quick: Invest in the right technology.
Circuit for Teams is one tool that can help.
Circuit for Teams plans the fastest sequence of delivery routes for drivers, saving managers the trouble of figuring it out.
By planning more efficient routes that can help you avoid roadblocks like traffic jams and construction sites, Circuit for Teams can help your delivery team save time and cut transportation costs.
Circuit for Teams also has other perks that can streamline your material handling.
You can set delivery time windows for customers and give real-time updates on a package’s process — increasing the likelihood that customers will be home to receive their goods.
This reduces the risk of failed deliveries and keeps customers happy. What’s better than that?



